Batch Script Files
Let's see how to create, save, execute, and edit batch files. In addition, DOs and DON'Ts suggestions are given.
Creating and Saving Batch Files
The easiest way to create a batch file is to use Notepad, but you can use any other text editor.
For example, let's try to create a basic batch file following these steps using Windows Notepad:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Notepad and click the top result to open the text editor.
-
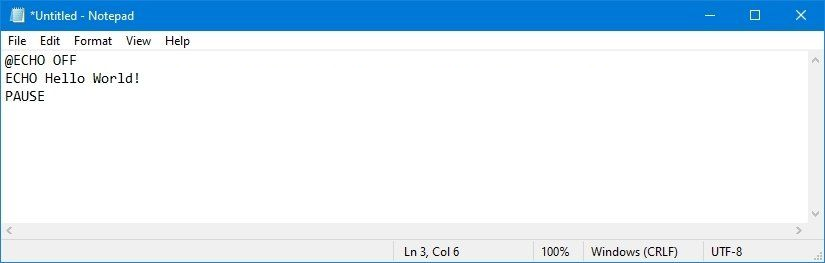
Type the following lines in the text file to create a batch file:
@ECHO OFF
ECHO Hello World!
PAUSEThe above script outputs the phrase, "Hello World! " on the screen.
@ECHO OFFShows the message on a clean line disabling the display prompt. Usually, this line goes at the beginning of the file. (You can use the command without the@symbol, but it's recommended to include it to show a cleaner return.)ECHOprints the text after the space on the screen.PAUSEallows the window to stay open after the command has been executed. Otherwise, the window will close automatically as soon as the script finishes executing.
-
Click the File menu, select the Save as option and confirm a name for the script (for example "first-script.bat")
You can use PAUSE command at the end of the script or after a specific command when running multiple tasks and want to pause between each line.
Some general rules to keep in mind when naming batch files
- Try to avoid spaces when naming batch files, because they sometimes create problems when called by other scripts.
- Don't name them after common batch files available in the system, such as ping.cmd.
Executing Batch Files
Once the batch file is created, simply double-click to run it.
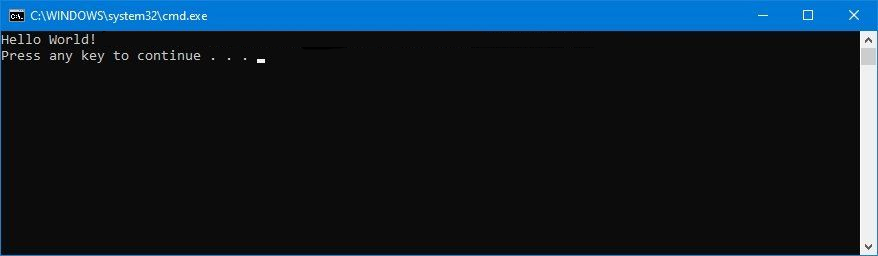
There are several ways to run a batch file:
- on-demand using the command prompt or the file explorer;
- on startup by defining a configuration to be performed at each startup;
- with Task Scheduler to automatically run the batch file at a specific time.
Modifying Batch Files
The easiest way to edit a batch file is to use Notepad, but you can use any other text editor.
Simply open the batch file with Notepad (or any other text editor), make the changes, and save.
Best Practice Suggestions
Programming best practices should always be followed when writing code, regardless of the programming language used.
DOs
- Documenting code with comments (see Batch Script Comments Chapter to learn more)
- Validating input
- Check variables before using them being sure that they are initialized.
- Indentation
DON'Ts
- Avoid one-line code (i.e. multiple command lines joined into a single line by ANDs and ORs) and use a block of code.
- Avoid nested block codes (nested if-else) and use subroutines instead.
- Don’t use variable names as command names