HTML introduction
HTML is an acronym which stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. HTML is used for creating web pages and web applications. Let's see what is meant by Hypertext Markup Language, and Web page.
Fundamental Terms
-
Hyper Text: HyperText simply means "Text within Text." A text has a link within it, is a hypertext. Whenever you click on a link which brings you to a new webpage, you have clicked on a hypertext. HyperText is a way to link two or more web pages (HTML documents) with each other.
-
Markup language: A markup language is a computer language that is used to apply layout and formatting conventions to a text document. Markup language makes text more interactive and dynamic. It can turn text into images, tables, links, etc.
-
Web Page: A web page is a document which is commonly written in HTML and translated by a web browser. A web page can be identified by entering an URL. A Web page can be of the static or dynamic type. With the help of HTML only, we can create static web pages.
Hence, HTML is a markup language which is used for describing the structure of a Web page.
An HTML document is made of many HTML tags and each HTML tag contains different content.
Example
Let's see a simple example of HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Web page title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Write Your First Heading</h1>
<p>Write Your First Paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document - The
<html>element is the root element of an HTML page - The
<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page - The
<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab) - The
<body>element defines the document's body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. - The
<h1>element defines a large heading - The
<p>element defines a paragraph
What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
<tagname>Content goes here...</tagname>
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<h1>My First Heading</h1><p>My first paragraph.</p>
| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
<h1> | My First Heading | </h1> |
<p> | My first paragraph. | </p> |
<br> | none | none |
Some HTML elements have no content (like the <br> element). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag!
Web browser
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
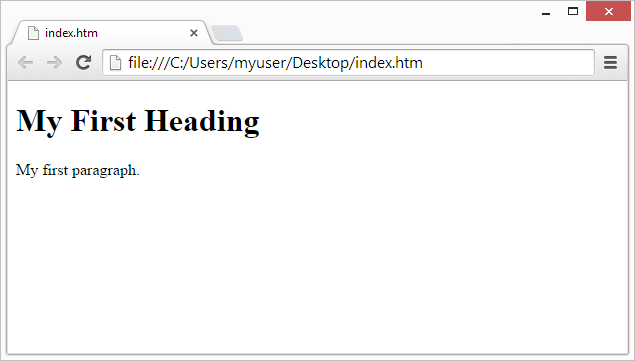
HTML Versions
Since the time HTML was invented there are lots of HTML versions in market, the brief introduction about the HTML version is given below:
-
HTML 1.0: The first version of HTML was 1.0, which was the barebones version of HTML language, and it was released in1991.
-
HTML 2.0: This was the next version which was released in 1995, and it was standard language version for website design. HTML 2.0 was able to support extra features such as form-based file upload, form elements such as text box, option button, etc.
-
HTML 3.2: HTML 3.2 version was published by W3C in early 1997. This version was capable of creating tables and providing support for extra options for form elements. It can also support a web page with complex mathematical equations. It became an official standard for any browser till January 1997. Today it is practically supported by most of the browsers.
-
HTML 4.01: HTML 4.01 version was released on December 1999, and it is a very stable version of HTML language. This version is the current official standard, and it provides added support for stylesheets (CSS) and scripting ability for various multimedia elements.
-
HTML5 : HTML5 is the newest version of HyperText Markup language. The first draft of this version was announced in January 2008. There are two major organizations one is W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), and another one is WHATWG( Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group) which are involved in the development of HTML 5 version, and still, it is under development.
Features of HTML
-
It is a very easy and simple language. It can be easily understood and modified.
-
It is very easy to make an effective presentation with HTML because it has a lot of formatting tags.
-
It is a markup language, so it provides a flexible way to design web pages along with the text.
-
It facilitates programmers to add a link on the web pages (by html anchor tag), so it enhances the interest of browsing of the user.
-
It is platform-independent because it can be displayed on any platform like Windows, Linux, and Macintosh, etc.
-
It facilitates the programmer to add Graphics, Videos, and Sound to the web pages which makes it more attractive and interactive.
-
HTML is a case-insensitive language, which means we can use tags either in lower-case or upper-case.
It is recommended to write all tags in lower-case for consistency and readability.